Three categories of cloud computing
- 📝 IaaS, PaaS, SaaS.
- Allows using a combination of these types of infrastructure.
- E.g. Microsoft 365 Apps on company computers (SaaS), VMs (IaaS) on Azure and Azure SQL Database (PaaS) to store your data.
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS)
- Instant computing infrastructure, provisioned and managed over the internet.
- Aims to give you the most control over the provided hardware that runs your application
- 📝 E.g. virtual machines (VMs), storage, and operating systems.
- You rent hardware instead of buying
- Ensuring that a service is up and running is a shared responsibility (see shared responsibility model)
- cloud provider ensures the cloud infrastructure is functioning correctly
- cloud customer ensures the service they are using is
- configured correctly
- up to date
- available to their customers.
Common IaaS use cases
- Migrating workloads: Managed similar to on-prem infrastructure & provides easy migration path.
- Test and development: Teams can quickly set-up & dispose test/dev environments with fast & economical scaling.
- Storage, backup and recovery: Organizations avoid the capital outlay and complexity of storage management.
- Useful for managing unpredictable demand and steadily growing storage needs.
- can also simplify the planning and management of backup and recovery systems.
Platform as a service (PaaS)
- Provides an environment for building, testing, and deploying software applications
- Can add features such authentication.
- Aims to help creating an application quickly without managing the underlying infrastructure.
- 📝 E.g. for a web app / Azure SQL databases you don’t need to install an operating system, web server, or even system updates.
- Resources are purchased on a pay-as-you-go basis and accessed over a secure Internet connection.
Common PaaS use cases
Development framework
- Lets developers create applications using built-in software components.
- 📝 Cloud features such as scalability, high-availability, and multi-tenant capability are included
- Reducing the amount of coding that developers must do.
Analytics or business intelligence
- Tools provided as a service with PaaS allow organizations to analyze and mine their data.
- They can find insights and patterns, and predict outcomes to improve business decisions such as forecasting, product design, and investment returns.
Software as a service (SaaS)
- Software that is centrally hosted and managed for the end customer.
- Usually based on an architecture where one version of the application is used for all customers
- Usually licensed through a monthly or annual subscription
- 📝 E.g. Office 365, Skype, and Dynamics CRM Online.
Cost and Ownership
| IaaS | PaaS | SaaS | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Upfront costs | None, pay for what you use | None, pay for what you use | None, monthly / annual subscription |
| User ownership | purchase, installation, configuration, and management of their own software, operating systems, middleware, and applications | development of their own applications | not responsible for any maintenance or management of that software. |
| Cloud provider ownership | underlying cloud infrastructure (such as virtual machines, storage, and networking) is available for the user. | operating system management, network, and service configuration.. typically everything except user application | provision, management, and maintenance of the application software |
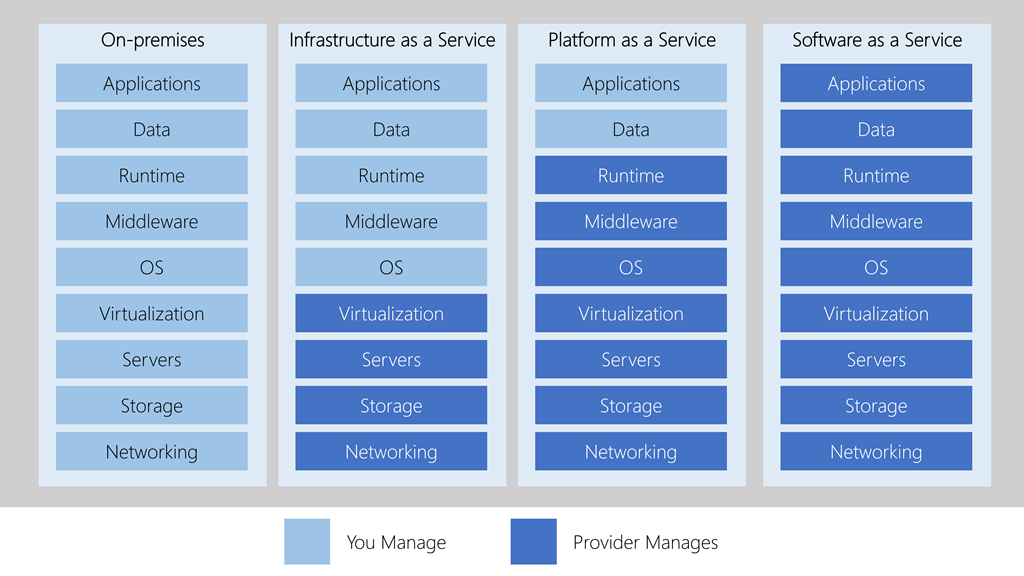
Management responsibilities
- These categories are layers on top of each other
- Abstraction order: SaaS > PaaS > IaaS
- Abstraction = Hide details, quicker production but less control over the underlying hardware.
- IaaS: user is responsible for managing the operating systems, data, and applications.
- PaaS: user is responsible for the applications and data they run and store.
- SaaS: user just uses the software.